Defining Money Management
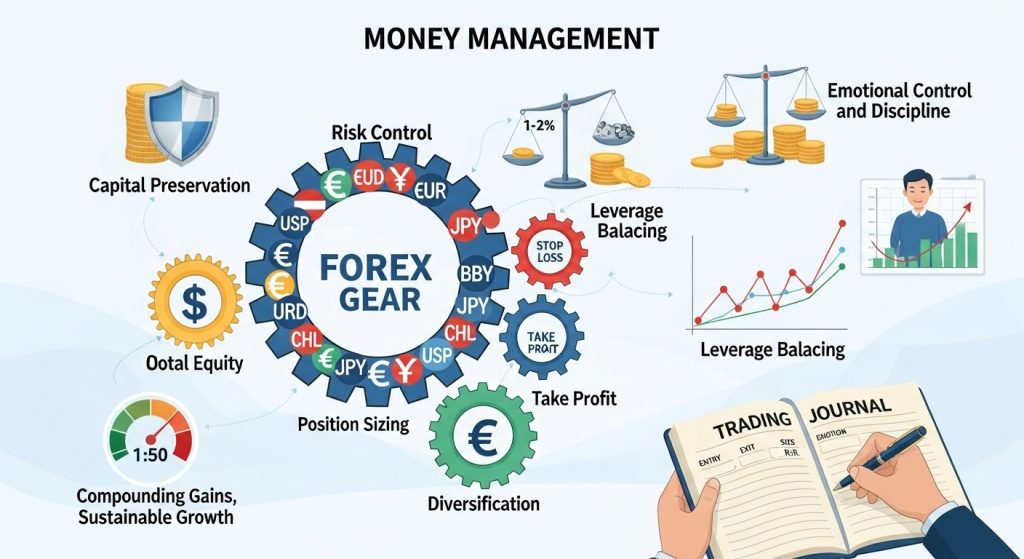
Money Management in the Forex market involves the disciplined handling of trading capital through risk controls, position sizing, and strategic planning. It sets clear rules for how much to risk per trade, how much to stay invested, and when to exit a position. Without robust money management, even the best Forex strategies can lead to catastrophic losses.
The Cornerstone of Capital Preservation
Preserving trading capital is the primary goal of Money Management. By limiting risk exposure on each trade—typically between 1% and 2% of account balance—traders prevent a string of losses from eroding their capital base. This safeguards the ability to stay in the market and recover from adverse moves.
 Risk per Trade: The 1–2% Rule
Risk per Trade: The 1–2% Rule
One of the most popular Money Management guidelines is the 1–2% risk rule. It dictates that no single trade should jeopardize more than 1–2% of total equity. This margin of safety ensures that even after multiple consecutive losses, a trader retains enough capital to continue trading without significant psychological or financial strain.
Calculating Position Size
Position size determines the amount of lots or units per trade and directly affects risk. Money Management requires adjusting position size based on account balance, stop-loss distance, and desired risk percentage. Precise position sizing allows traders to scale their exposure up or down while maintaining consistent risk parameters.
Implementing Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders
Stop loss and take profit orders are fundamental Money Management tools. A stop loss automatically closes a trade when a predetermined loss level is reached, preventing runaway losses. Conversely, a take profit order locks in gains when the market hits a target. Consistent use of these orders removes emotional bias from exit decisions.
The Leverage Balancing Act
Leverage amplifies both profits and losses. Money Management strategies emphasize prudent leverage use, often recommending ratios no higher than 1:50 for retail traders. Excessive leverage can quickly deplete capital during volatile swings, whereas moderate leverage allows for manageable drawdowns.
Importance of Diversification
Diversification spreads risk across multiple currency pairs and uncorrelated assets. Effective Money Management involves avoiding over-concentration in a single pair or correlated instrument. By diversifying, a losing trade in one market segment can be offset by gains in another, smoothing equity curves over time.
 Building a Trading Plan
Building a Trading Plan
A comprehensive trading plan integrates Money Management rules with entry, exit, and market analysis strategies. It documents risk tolerance, allowed leverage, maximum daily loss limits, and performance benchmarks. Following a written plan reduces impulsive decisions and reinforces disciplined Money Management practices.
Emotional Control and Discipline
Psychology plays a critical role in Money Management. Fear and greed often lead traders to deviate from risk rules, increasing position sizes after losses or moving stop losses. Cultivating emotional discipline ensures adherence to Money Management guidelines, fostering consistent, rational decision-making.
Tracking Performance with a Trading Journal
Maintaining a trading journal supports continuous improvement of Money Management. Recording every trade’s entry price, exit price, position size, risk-to-reward ratio, and emotional state helps identify patterns. Analyzing journal data refines risk controls and identifies areas for adjustment.
Compounding Gains for Sustainable Growth
Compounding is the process of reinvesting profits to increase trading capital gradually. By applying Money Management rules consistently to a growing account balance, traders can accelerate returns over time. Patience and a conservative compounding approach protect against overtrading and large drawdowns.
Continuous Review and Adaptation
Markets evolve, and so should Money Management strategies. Periodic review of risk parameters, position-sizing methods, and stop-loss techniques helps adapt to changing volatility, economic conditions, and personal trading goals. Ongoing refinement ensures that Money Management remains aligned with performance objectives.
Final Thoughts
Implementing robust Money Management practices transforms Forex trading from speculative gambling into a structured, strategic endeavor. By prioritizing capital preservation, controlling risk per trade, and balancing leverage, traders can navigate market fluctuations with confidence and achieve sustainable growth.